Schema
JAMstack
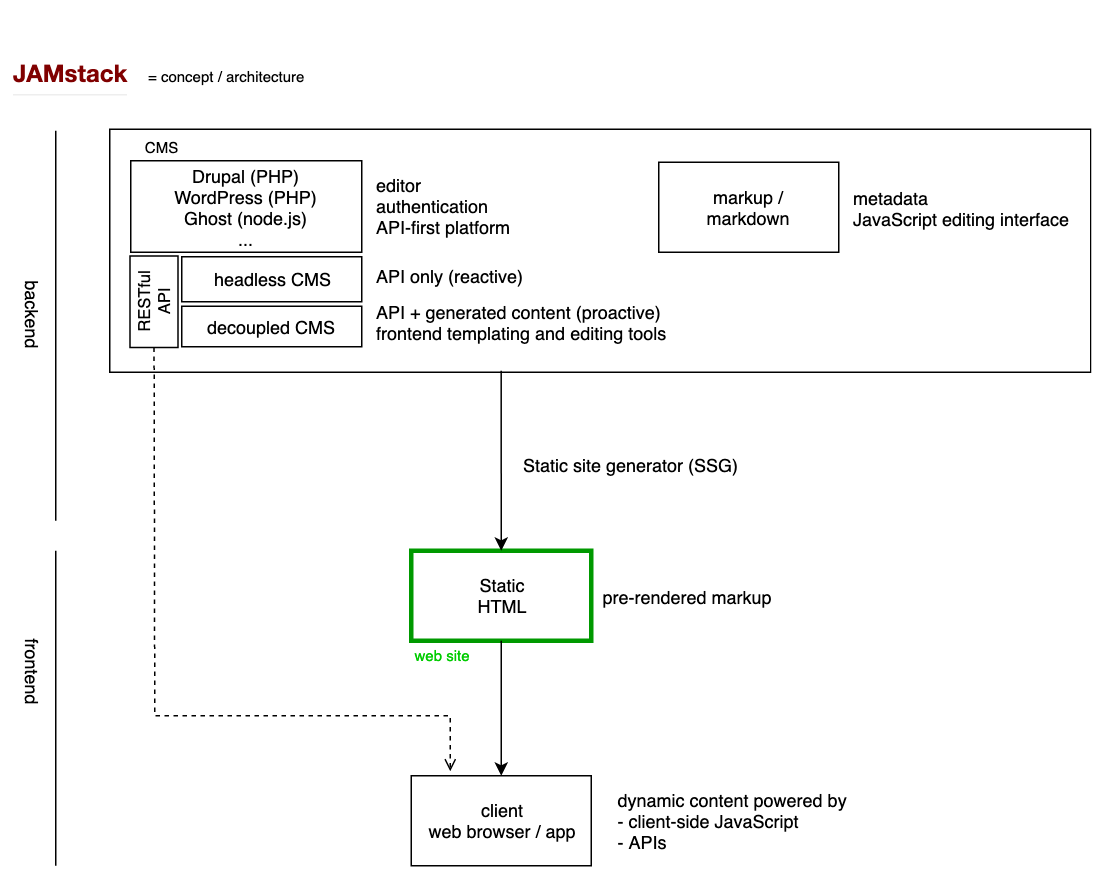
JAMstack is a concept / architecture for a web stack based on client-side JavaScript, APIs and pre-rendered Markup.
The core of this concept is the pre-rendered static web site in HTML.
In combination with client-side technologies like:
- dynamic content powered by JavaScript
- client-side APIs
- consulting server-side APIs (RESTful API CMS / web services)
Mostly we can divide the web stack in 3 parts:
- Content is stored in
- a headless or decoupled CMS
- markdown with metadata in front matter
- markup with metadata (ex. HTML with metadata in comments or meta property attributes)
- JSON data files
- ...
- A static site generator (SSG) to generate the static HTML pages.
- The static generated HTML pages (frontend web site)
Headless vs decoupled CMS
A headless CMS only provides content/data with a RESTfull API. No content is
pre-rendered
A decoupled CMS is a headless CMS with the addition of pre-rendering static pages, and on
the backend CMS: templates, editing interface, authentication, ...
Static site generators
A lot of static site generators (SSG) exist to simplify the task to generate static HTML pages.
- Jekyll (ruby, supported by GitHub)
- Gatsby.js (Node.js JavaScript, React, GraphQL)
- Eleventy (Node.js JavaScript)
- Hugo (golang)
- ...
Or write it in the programming language you already use
- PHP
- JavaScript
- ASP
- ...
Using a template engine
- Twig (PHP)
- Liquid (Ruby)
- EJS (JavaScript)
- Handlebars.js
- ...
Limitations / advantages
JAMstack eliminates limitations from a traditional coupled (monolithic) CMS system
Advantage:
- performance
- security
- reduced complexity
- no critical updates
- web site not going offline / maintenance
- low cost scaling
- simple caching
- removes lots of points of failures
- can serve more connections
- usable in CDN (content delivery network)
Disadvantage:
- Some functionalities provided by a CMS out of the box or with plugins must be programmed or by using an external API provider that most likely isn't free.